When NASAlaunched a spacecraft to an asteroid,Watch Sexy Beggars Pudding Online scientists patiently waited for their chance to look at bits of the spacerock in a laboratory, hoping it would answer some of humanity's most enduring questions.
For Danny Glavin, a senior sample scientist, he wanted to solve a relentless mystery in his life's work: Why are all known living things only based on the left-handed forms of amino acids, the molecules that build proteins?
His moment arrived nearly a decade later. Glavin and a team of researchers probed the grit from Bennu, a carbon-rich asteroid made of loosely bound boulders, but what they found threw them a curveball. Rather than supporting one of the leading hypotheses — that the early solar system favored the left-handed variety and brought those ingredients to primitive Earth — it showed no favoritism at all.
"I have to admit, I was a little disillusioned or disappointed," Glavin said. "I felt like this invalidated 20 years of research in our lab and my career."
SEE ALSO: NASA's asteroid sample reveals key chemistry that could lead to life Researcher Jason Dworkin holds up a vial containing a Bennu sample. Credit: NASA / James Tralie
Researcher Jason Dworkin holds up a vial containing a Bennu sample. Credit: NASA / James Tralie Many amino acids, whether they're used in biology or not, come in two mirror-image forms. Each molecule has a central carbon atom with other atom groups attached, oriented in one direction or the reverse. This property, called chirality, is like a left and right hand: They're similar, but if you stacked them, the thumbs would be hitchhiking opposite ways.
In Earth life, the amino acids are always "left-handed," and sugars, which partly make up the backbone of DNA, are always right-handed, giving the double helix its signature twist to the right. The homogeneity found among both is especially confounding to scientists because the left and right-handed versions of all these molecules are equally available in nonliving chemical mixes.
Practically speaking, if all biological molecules took the reverse form, that might work just fine. So if life could have taken the other path, why didn't it? Is uniform "handedness" a secret ingredient in the recipe for life, and more specifically, did it haveto turn left? Did the bias toward left-handed amino acids begin in the cosmos, or did it happen later on this planet?
"A fundamental question for all of us is whether life had to be the way it is," said Irene Chen, professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at UCLA, who wasn't involved in the asteroid study. "Is the universe predisposed to our kind of life, or is our biology the result of accidents and chance?"
 NASA chose carbon-rich asteroid Bennu to study the chemical origins of life. Credit: NASA
NASA chose carbon-rich asteroid Bennu to study the chemical origins of life. Credit: NASA Scientists knew early on they would use the material collected by NASA's $800 million OSIRIS-Rex mission, short for Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, and Security-Regolith Explorer, to analyze the "handedness" of individual amino acids. Bennu's mineral fragments could be older than the 4.6 billion-year-old solar system. These grains of stardust could have come from dying starsor supernovasthat eventually led to the creation of the sunand planets.
To do their study, they brewed a sort of "Bennu tea," boiling a small amount of the rocks and dust in water and acids to extract organic compounds. Then they used mass spectrometry techniques to identify organic molecules, including 14 of the 20 amino acids life uses to build proteins, which carry out genetic instructions. Some of the latest findingswere published this week in the journal Nature Astronomy.
"I have to admit, I was a little disillusioned or disappointed. I felt like this invalidated 20 years of research in our lab and my career."
Over the past few decades, researchers have found that meteorites— rocks that have traveled space and crash-landedon Earth — have had a higher concentration of left-handed amino acids than right-handed ones, in the neighborhood of 60 percent more. Perhaps space rocks delivered the compounds that then underwent chemical reactions near Earth's deep-sea ventsto form the first cells. The rest is evolution, perhaps.
Those results, coupled with the knowledge that space rocks have bombarded the planet for eons, have led scientists to believe ancient asteroids, the solar system's time capsules, would also reveal more left-handed amino acids. If the solar system indeed harbors more lefties, perhaps polarized light in space was the culprit. A slight favoritism in the environment could turn into a larger disparity over time.
 Scientists think meteorites and planetary body collisions may have delivered origins of life chemistry to early Earth, including left-handed amino acids. Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Conceptual Image Lab illustration
Scientists think meteorites and planetary body collisions may have delivered origins of life chemistry to early Earth, including left-handed amino acids. Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Conceptual Image Lab illustration But the Bennu researchers found lefties and righties comingling equally. Now Glavin wonders if the previous studies on meteorites are invalid, perhaps contaminated with Earth proteins when they fell to the ground. Jason Dworkin, project scientist for the OSIRIS-Rex mission, thinks there may be a different reason for Bennu bucking the trend.
"Bennu is an example of one type of future meteorite which is too fragile to survive landing on Earth, and so it's not really in our collections," Dworkin said.
Maybe the reality is that life's design was determined by a coin flip. Once a successful pattern was established, the template continued through evolution. Proteins and enzymes, tiny drivers inside cells, fit together like a jigsaw puzzle. If life emerged with left-handed amino acids, switching to right-handed amino acids later might have stopped everything from working. There are vast advantages to uniformity: If people were based on right-handed amino acids, they wouldn't be able to eat and digest plants or animal products based on left-handed amino acids.
Researchers have made mirror versions of biological proteins with right-handed amino acids in a lab. They function similarly, but they're much harder to destroy. Enzymes that would typically break them down are rendered useless. Like your hair dryer on an international vacation, the tool won't work if the plug and outlet don't match.
 A diagram of a left-handed and right-handed version of an amino acid from a meteorite. Credit: NASA illustration
A diagram of a left-handed and right-handed version of an amino acid from a meteorite. Credit: NASA illustration Some scientists considering the implications of this problem have expressed concerns about the future development of mirror cells in laboratories. If people became infected with harmful mirror bacteria, their immune systems might be defenseless, unable to wage any sort of counterattack. A group of biologists recently wrote an extensive paperon the risks, as reported by The New York Times.
Despite Glavin's disappointment that Bennu didn't present a chirality bias, the research continues. He and his collaborators plan to study more samples of the asteroid to investigate other amino acids' handedness.
And there might be a silver lining: Some astrobiologists have proposed using disproportionate handedness of molecules as a biosignature. An even mix of both types in an extraterrestrial sample might suggest molecules were made chemically without the involvement of living things. But an excess of one type could be a clue for alien life.
"Frankly, it actually might make the search for life easier in some respects because we don't have this risk potentially of a false positive," Glavin said. "We (could) believe that if there's an amplification of one or the other, that there may be biology behind it."
UPDATE: Feb. 3, 2025, 4:28 p.m. EST An earlier version of this story used an incorrect first name for a professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at UCLA. Her name is Irene Chen.
Topics NASA
 Amazon Spring Sale 2025: Best LG OLED TV deal
Amazon Spring Sale 2025: Best LG OLED TV deal
 Bona Nit, Estimat (An Ordinary Night) by Robert Glück
Bona Nit, Estimat (An Ordinary Night) by Robert Glück
 The Review’s Review: Real Housewives Edition by The Paris Review
The Review’s Review: Real Housewives Edition by The Paris Review
 In the beginning is the end by Meret Oppenheim
In the beginning is the end by Meret Oppenheim
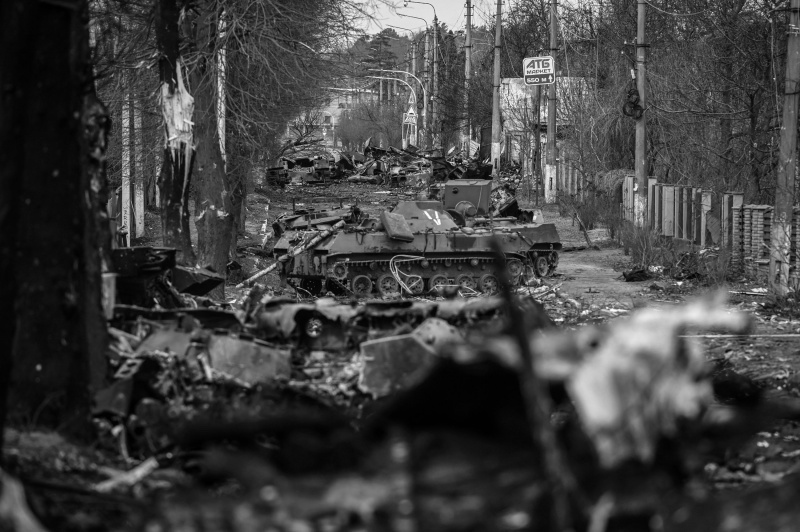 In Occupied Cities, Time Doesn’t Exist: Conversations with Bucha Writers by Ilya Kaminsky
In Occupied Cities, Time Doesn’t Exist: Conversations with Bucha Writers by Ilya Kaminsky
 Bona Nit, Estimat (An Ordinary Night) by Robert Glück
Bona Nit, Estimat (An Ordinary Night) by Robert Glück
 The Distance from a Lemon to Murder: A Conversation with Peter Nadin by Randy Kennedy
The Distance from a Lemon to Murder: A Conversation with Peter Nadin by Randy Kennedy
 In Remembrance of John Train, 1926–2022 by The Paris Review
In Remembrance of John Train, 1926–2022 by The Paris Review
 Amazon Spring Sale 2025: Best LG OLED TV deal
Amazon Spring Sale 2025: Best LG OLED TV deal
 Softball Season by Sophie Haigney
Softball Season by Sophie Haigney
 Love, Loosha by Lucia Berlin and Kenward Elmslie
Love, Loosha by Lucia Berlin and Kenward Elmslie
 Bona Nit, Estimat (An Ordinary Night) by Robert Glück
Bona Nit, Estimat (An Ordinary Night) by Robert Glück
 You won't see Elon Musk smoking weed in public again, NASA admin says
You won't see Elon Musk smoking weed in public again, NASA admin says
 On Penumbra, Caio Fernando Abreu, and Alain Mabanckou by The Paris Review
On Penumbra, Caio Fernando Abreu, and Alain Mabanckou by The Paris Review
 Desolation Journal by Jack Kerouac
Desolation Journal by Jack Kerouac
 Clipboard, 2022 by Jesse Ball
Clipboard, 2022 by Jesse Ball
 New York Film Festival Dispatch: Cold War Movies by The Paris Review
New York Film Festival Dispatch: Cold War Movies by The Paris Review
Miss Texas gives a far better answer on Charlottesville than TrumpFacebook is dropping $1 billion on video, and that's pretty great newsEquifax hit with $70 billion classGoogle's newsSloane Stephens just won a lot of money at the U.S. Open but her reaction is pricelessRED reveals how the 'holographic display' in its Hydrogen phone worksGal Gadot shares the most delightful 'Wonder Woman' blooper reel'Will and Grace' has a GIF collection nowApple gives $5 million to hurricane relief, will activate donations through iTunesChrissy Teigen liveSnapchat's newest media partners: college newspapersFacebook is dropping $1 billion on video, and that's pretty great newsScandal prompts FTC to crack down on social media influencers'Game of Thrones' Season 8 theory suggests Melisandre might save Dany'Super Mario 64' is now an online gameAlamo Drafthouse's clownSurreal images show the turbulent ocean through the eye of a hurricaneWith Irma about to slam their office, National Hurricane Center employees stay to workThe year of Wonder Woman continues with the excellent 'Professor Marston''Game of Thrones' Season 8 theory suggests Melisandre might save Dany New Star Wars film might include Princes Harry and William Game of Thrones: A dragon dies in 'Beyond the Wall,' but it gets worse The New York Times has recognized that it did not discover bubble tea The solar eclipse shows up beautifully in weather forecast models You'll want to swipe right on our Tinder profiles for 'Game of Thrones' characters 13 times 'The Defenders' roasted Iron Fist so you wouldn't have to Google Home will now play free Spotify accounts You can pre 'Game of Thrones' reunions we're still waiting for Download this: Off the Menu Club is the answer to all your foodie prayers Essential Phone review: Super slick, but not an iPhone or Pixel killer Live your laziest life with this super convenient charging pad Elisabeth Moss says 'Handmaid's Tale' Season 2 will 'blow people away' 'Planet of the Apps' was a successful disaster Stunning new view of Jupiter flips Great Red Spot on its side How 'StarCraft II' is powering a clever HD remake of 'Diablo II' Dating apps are now banning white supremacists 'Game of Thrones': 6 ways to transport White Walkers south of the wall Consumer Reports is wrong about Microsoft’s Surface products Leaked images show off one of the iPhone 8's key components
2.2969s , 10183.109375 kb
Copyright © 2025 Powered by 【Watch Sexy Beggars Pudding Online】,Charm Information Network